SMS and iMessage are two popular ways people send messages every day. While both help us stay connected, they work very differently. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best option for your needs.
SMS uses your mobile network and works on all phones, including Android and iPhone. iMessage uses the internet and works only on Apple devices. Because of this, features, security, and costs can vary a lot.
In this article, we explain SMS vs. iMessage in simple terms. You’ll learn how each works, their pros and cons, and which option fits personal or business communication better.
SMS vs. iMessages: Key Differences

The key differences between SMS vs iMessage come from how messages are sent and who can receive them. SMS messaging uses cellular networks and works on all phones, while iMessage relies on internet data and supports end-to-end encryption, rich media, and Apple-only features.
What is SMS?
SMS, or Short Message Service, is a basic way to send text messages using cellular networks. It works on all mobile phones and does not need internet access. Because of this, SMS remains a reliable and widely used texting method.
Moreover, SMS messaging sends messages directly between phone numbers, making it compatible with every carrier. Messages are limited to 160 characters, and longer texts are cut automatically. This simple system ensures messages reach users almost anywhere.
However, SMS supports only plain text. When you send photos or videos, phones switch to MMS messaging. Even so, SMS continues to be useful for alerts, proof codes, and important communication where internet access is unavailable.
What is iMessage?
iMessage is Apple’s internet-based messaging service that works only within the Apple ecosystem. It lets iPhone, iPad, and Mac users send messages using WiFi or mobile data, instead of cellular networks.
In addition, iMessage messaging supports unlimited text length, high-quality photos and videos, read getting, and typing indicators. Messages sync automatically across Apple devices, creating a smooth and connected communication experience.
Most importantly, iMessage uses end-to-end encryption to protect conversations. This means only the sender and receiver can read messages. As a result, iMessage offers stronger privacy and security than traditional SMS texting.
What is the Difference Between iMessage and SMS?
The difference between iMessage and SMS lies in delivery and features. iMessage uses internet data with end-to-end encryption, while SMS messaging relies on cellular networks and supports only basic text communication.
Transmission and network
Transmission and network explain how messages travel. SMS messaging sends texts through cellular networks, so it works without internet access. In set off, iMessage uses WiFi or mobile data, routes messages through Apple servers, and delivers faster when internet connections are strong.
Device compatibility
Device compatibility shows who can receive your messages. SMS messaging works on all mobile phones and carriers, including Android and iPhone. In contrast, iMessage only functions within the Apple ecosystem, limiting communication to iPhone, iPad, and Mac users.
Security and encryption
Security and encryption play a major role in messaging safety. iMessage security uses end-to-end encryption, so only the sender and receiver can read messages. This protects conversations from carriers, hackers, and unauthorized access.
In contrast, SMS messaging does not offer encryption and travels through cellular networks. As a result, messages may be intercepted or accessed by third parties. Therefore, SMS is less secure for sharing sensitive information.
Features and multimedia
Features and multimedia set iMessage apart from SMS. iMessage messaging supports unlimited text, high-quality photos and videos, read receipts, typing indicators, and message effects, creating a rich communication experience.
On the other hand, SMS messaging is limited to 160 characters and basic multimedia through MMS, which often compresses files and reduces quality, offering a simpler, more basic messaging option.
Cost structure
The cost structure differs between SMS and iMessage. SMS messaging may charge per message or require a texting plan from your carrier. MMS messages with photos or videos often cost more than standard texts.
In contrast, iMessage is free to use over WiFi or mobile data. It does not incur per-message charges, making it more cost-helpful, especially for sending high-quality media or long messages between Apple devices.
What’s the Better Option for Business Use?
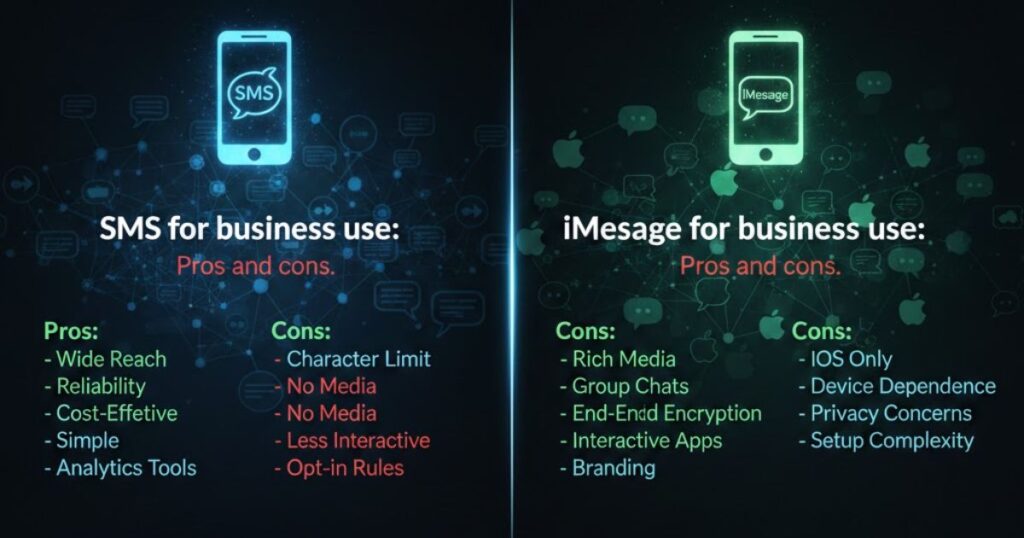
For businesses, choosing between SMS vs iMessage depends on security, features, and compliance. iMessage offers end-to-end encryption and rich media, improving communication, while SMS messaging ensures universal reach across all devices, making both valuable when used strategically.
SMS for business use: Pros and cons
Advantages:
- SMS messaging works on all phones, ensuring universal communication with clients and employees.
- Businesses can rely on carrier-based texting without needing internet access.
- Costs are predictable with per-message or bulk SMS pricing plans.
- Simple setup allows easy integration into existing business workflows.
Disadvantages:
- SMS messages are not encrypted, creating potential security risks for sensitive information.
- Limited to 160 characters, restricting message length and detail.
- Multimedia sharing via MMS can be costly and lower quality.
- Lacks modern features like read receipts, typing indicators, or rich media.
iMessage for business use: Pros and cons
Advantages:
- iMessage provides end-to-end encryption, keeping business communication secure from cyber threats.
- Supports rich media, read receipts, and typing indicators, improving collaboration and productivity.
- Cost-effective when using existing WiFi or mobile data infrastructure.
- Familiar interface encourages better employee adoption and engagement.
Disadvantages:
- Works only within the Apple ecosystem, limiting communication with non-Apple users.
- Traditional compliance and archiving can be challenging without proper tools.
- Requires specialized message routing for business oversight.
- Dependence on internet connectivity may cause delays in areas with poor data coverage.
Overcoming iMessage Compliance Barriers

Businesses once struggled to use iMessage due to its end-to-end encryption, which made archiving and compliance difficult. However, modern tools now capture and store iMessages securely, allowing companies to meet regulatory requirements without compromising privacy.
Advanced mobile archiving platforms can preserve iMessage metadata, including timestamps, party, and delivery status. This ensures legal ediscovery and message retention, making iMessage a viable option for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
By integrating iMessage with existing compliance management systems, organizations can automate data retention policies. This talk maintains security, enhances productivity, and meets industry-specific regulatory standards, removing previous barriers to adopting iMessage for business use.
Essential Compliance Features Currently Supported for iMessage:
- Complete message capture and preservation for legal ediscovery
- Metadata retention including timestamps, participants, and delivery status
- Integration with existing compliance management systems
- Automated data retention policies meeting industry-specific requirements
With proper tools, businesses can safely use iMessage messaging for communication. Security, privacy, and compliance happen, allowing companies to benefit from modern features while meeting legal obligations.
Summary of the Main Points
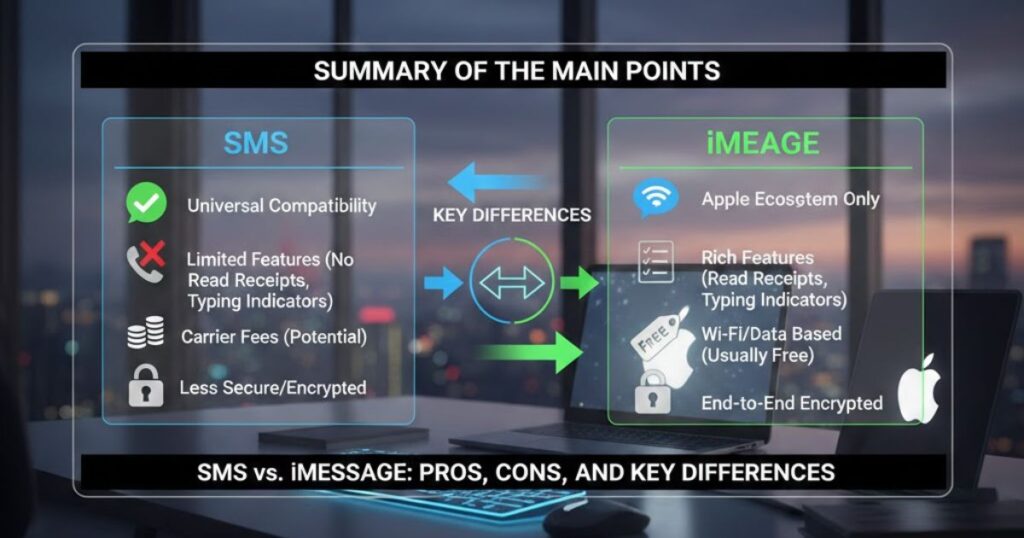
SMS vs iMessage use different technologies: SMS messaging relies on cellular networks, while iMessage sends messages through the internet using WiFi or mobile data.
Device compatibility varies: SMS works on all phones and carriers, whereas iMessage is limited to iPhone, iPad, and Mac within the Apple ecosystem.
Security and encryption differ notably: iMessage offers end-to-end encryption, protecting messages, while SMS lacks encryption, making it less secure for sensitive information
Features and multimedia set them apart: iMessage supports unlimited text, high-quality photos, videos, read getting, and typing indicators, whereas SMS messaging is limited to plain text and basic MMS attachments.
Cost structure matters: SMS may charge per message or require a texting plan, while iMessage uses WiFi or mobile data, avoiding per-message fees and making it more cost-effective for heavy messaging.
Business use considerations show a trade-off: SMS messaging ensures universal reach and simple archiving, while iMessage provides better security, advanced features, and modern workflow integration, requiring proper compliance tools.
FAQ
Is it an iMessage SMS?
No, iMessage is not SMS. It uses internet data and works only on Apple devices, unlike cellular-based SMS messaging.
Why should someone use SMS instead of iMessage?
SMS messaging works on all phones, including Android, and delivers texts reliably even without internet or Apple devices.
Should I have SMS turned on an iPhone?
Yes, enabling SMS messaging ensures fallback texting when iMessage is unavailable, like poor internet or messaging non-Apple users.
Can I send iMessages on an Android phone?
No, iMessage only works between Apple devices. Android users receive texts as SMS or MMS instead.
How do I know if it’s an iMessage or text?
iMessages appear blue in the Messages app, while SMS messaging shows green bubbles on an iPhone.
What should businesses know about iMessage compliance?
Businesses must use proper archiving tools to capture and manage iMessage messaging, meeting retention, ediscovery, and regulatory requirements.
Can I send iMessages to a group that includes Android users?
No, including Android users converts the group chat to SMS/MMS, removing iMessage features like read getting or media quality.
Do I need a phone number to use iMessage?
No, you can use iMessage with just an Apple ID email on iPad or Mac without a phone number.
Are there any specific regulations that highlight the need for iMessage archiving?
Yes, finance, healthcare, and government rules require archiving iMessage communications for legal, retention, and compliance purposes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SMS vs iMessage offers different benefits depending on your needs. SMS messaging provides universal compatibility, reliability, and simple delivery across all devices, making it key for reaching everyone. Meanwhile, iMessage excels within the Apple ecosystem, offering end-to-end encryption, rich media, read receipts, and seamless syncing.
For businesses, choosing between the two depends on security, compliance, and functionality. Modern archiving tools now allow secure iMessage messaging while meeting regulatory requirements. Ultimately, understanding the differences, costs, and power ensures smarter communication, whether for personal use or professional business purposes, giving users give and order in messaging.
Read More Articles: Msgsword



